Corporate Bond Sales Near Record — U.S. corporate bond issuance has surged toward record levels this year, driven by borrowing to fund AI and tech growth.

Corporate Bond Sales Near Record: The Role of Tech and AI Growth in Triggering the US Borrowing Boom
A Historic Surge in Corporate Bond Issuance

In the recent years, the global financial environment has been experiencing a rapid shift, but there is nothing as remarkable as the increase of corporate bond offerings by US companies. The corporate bond market in the US is approaching a record high due to a mix of factors including technological revolution and corporate strategic planning. At the center of this wave is the tremendous growth of Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Computing, Data Centers, and other advanced technologies, which have an immediate capital need of an unprecedented kind. Companies, especially in the technologically-driven industries, are increasingly resorting to the bond market as a way of raising long-term capital at a relatively known cost while at the same time fundamentally impacting the corporate balance sheets as well as the overall economy in a significant way.
Understanding Corporate Bonds and Their Significance
Corporate bonds are the type of debt offered by companies as a means of raising funds. In this process, the company undertakes to offer periodic interest, also known as coupons, as well as the face value at the end of the loan term. As opposed to stock, issuing bonds does not dilute the company’s stock, making it an appealing way for companies to raise funds without giving up control. Corporate bonds are an important component of the modern financial system, serving as a conduit for investment savings, including funds from pension funds, insurers, and mutual funds, into the economy. The scale of the U.S. corporate bond market, already the largest globally, indicates the complexity of the financial markets in the United States.
Scale of the Current Issuance Boom
This spurt of bond issuance is remarkable not only for its scale but also for its speed. corporations are raising funds from bond issuances at a speed that is rivaling or exceeding records set during times of economic recovery and/or lower interest rates. Investment-grade companies, especially from the technological sector, have been leading this charge, although high-yield bond sales are also rising. This level of borrowing shows that corporates have/had strong conviction that future cash returns can cover loan repayments notwithstanding an uncertain economic outlook and/changed monetary policies.
Artificial Intelligence in Financing and Lending Activity
Artificial intelligence technology has proved to be one of the strongest fund drivers for corporations in recent years. Implementing and developing artificial intelligence technology involves huge capital outlays, including investments in “specialized chips and high-quality data centers.” Tech leaders and even conventional firms using artificial intelligence technology solutions must shell out huge amounts before seeing a return on their investment. Corporate bonds serve as a viable means for financing such long-term projects. As artificial intelligence technology plays a crucial role in competitiveness in all fields, firms are even treating borrowing as a “strategic necessity and not as a risk due to rivalry factors.”
Growth in Data Centers and Infrastructure
One of the most capital-intensive areas related to the development of AI involves the data centers industry. This follows the fact that the type of computing power employed by the AI systems is huge and therefore needs a lot of electricity and the latest technology. Developing data centers takes billions of dollars, to say the least, over a long period of time. Companies that issue bonds, therefore, are able to lock in funding that takes the same time to repay the debt, which closely relates to the long-life nature of the project.
Favorable Market Conditions for Issuers
Market conditions
Market conditions have been another important contributor for the promotion of corporate bond issuance. Fluctuating interest rates notwithstanding, the market for high-grade corporate bonds remains robust. The volatility witnessed in the equity markets prompted investors looking for steady income sources to turn to the bond market, resulting in conducive pricing for corporations looking to tap this market. The credit spread, which measures the differential between corporate bond yields and government bond yields, remains sufficiently manageable, a good indicator for corporate creditworthiness.
Federal Reserve Policy & Interest Rate Dynamics
The monetary policy in the US has played an important role in shaping the borrowing decisions of corporations. Although interest rates have gone up, as they are no longer ultra-low as in the period of the pandemic, corporations still consider them to be manageable, especially in light of strong earnings and cash positions. Other corporations decided to tap the market aggressively ahead of possible interest rate increases. The strategy of Fed communication has played an indirect role in shaping corporate borrowing.
Change in Corporate Financing Policies
A rise in the number of bonds issued can also be attributed to a paradigm shift in corporate funding dynamics. Today, firms are actively engaged in managing their capital structure and issuing bonds not just for funding, but also for creating flexibility in their capitals. Certain corporate entities may use bonds for refining existing debts, extending the maturity, or even creating liquidity buffers. Other firms might seize appropriate market opportunities to pre-fund expenditures that could be made in the future.
Dominance of Technology and Mega-Cap Stocks
As mentioned
The tech giants are also at the forefront of the bond issuance boom. Firms that deal in software, semiconductors, cloud solutions, and AI platforms enjoy great credit ratings, thus allowing them to borrow money at low costs. Such firms usually engage in issuing bonds in the order of billions of dollars, which can easily be syndicated away. The size of such firms, coupled with their global reach, makes them dependable for borrowing money. In addition, their expansion opportunities, which are AI-related, increase their appeal to investors.
Representation from Non-Tech Industries
Although the tech industry makes the most headlines, other industries have been contributing in a substantial manner to this increase as well. The increased participation in the bond market includes manufacturing companies pursuing automation, health care companies pursuing the application of AI in diagnostics, banks pursuing upgrades in their online platforms, as well as the energy industry supporting the increased demand for data center power.
Investor demand and portfolio composition
Demand from investors is an important driving force for the record levels. Institutional investors such as pension funds and insurance companies demand a source of steady income over a long-term horizon. Corporate bonds, and investment-grade bonds in particular, are a good fit for such demands. While sovereign bond market rates keep varying, and the equity markets remain volatile, corporate bonds provide a sensible spread. The vast demand creates a scenario where a large amount of debt issuance becomes possible with little impact on spreads, pushing the trend further.
Associated Risks of Increased Corporate Debt
In contrast to the encouraging scenario, the increased number of corporate bond issuances has raised leverage concerns. Too much leverage could become burdensome for companies if economic conditions become unfavorable or if their projected incomes are compromised. Firms that actively pursue AI-related projects could encounter delayed returns, potentially causing cash flow divergences. Rating agencies are particularly attentive to leverage ratios; excessive leverage could result in downgrades, which in turn would increase future borrowing costs.
Possible Effects of Economy Slowdowns
The slowing economy could be considered a major risk factor in the current borrowing frenzy. It could mean lower profits for businesses, leading to difficulties in servicing debts. This would especially impact high-yield borrowes, who would be working with small margins. Even though investment-grade firms tend to have stronger balance sheets, economic troubles could impact the corporate bond market, leading to higher defaults and greater market volatility.
Comparison of Current Issuance Cycle with Historical Ones
Historically, corporate bonds have seen a huge spike during economic recoveries and low-interest rates. The difference in this cycle is that it is driven by technological changes and less by economic recoveries or low rates. Technological changes drive AI adoption as it is a technological shift and not an economic stimulus because it is a permanent revolution as opposed to economic recoveries that are short-term events.
Implications on Financial Markets
Investors
Financings by non-financial corporations in this environment carry significant market implications. This affects the yield curve, which may, in turn, be affected by the supply of bonds. Demand for bonds has been robust, but this does not necessarily mean that a market change in investor appetite may not occasion market volatility. There may be increased concentration risks in fixed income related to the prevalence of technology bonds.
Impact on the Overall Economy
In terms of macroeconomic policy, the boom in borrowing is supportive of investment, employment, and productivity increase. The proceeds of the bond market help the innovational, infrastructural, and expansionary needs of businesses, which boost economic growth. Investment in AI can help improve the efficiency of the different business sectors; hence, the beneficial outcomes of the project would result in increased outputs or gains in the long run and requires proper financial management.
RTCA AND FAEs: REG
Debt markets and regulations related to corporate debt are also monitored carefully by regulatory authorities and governments. Though leverage helps in the development of a country, excessive leverage can be a source of danger for financial systems. So, stress tests, disclosure obligations, and prudent regulation can help assure proper risk management by firms and financial entities. A balance between promoting investment and securitization linked to innovation and safeguarding the financial systems is required.
International Effects of U.S. Corporate Borrowing
The U.S. corporate bond market has global ramifications. The international investment community has significant holdings of U.S. corporate debt. The reason for this is the depth of the U.S. capital markets and investment quality. However, global capital flows and exchange rates are impacted by the rising trend in new issuance. The impact of U.S. corporations borrowing money for AI research has global implications in terms of global competition.
Outlook for the Future: Corporate Bonds
In the wake of Looking forward, the trend of corporate bond issuance is expected to remain strong, but only if the investment momentum of AI and digitalization continues. However, if interest rates rise considerably or if the overall macroeconomic environment turns weak, then the growth of corporate bond issuance is expected to slow. Moreover, organizations can also explore different funding options, including equity issuance or partnerships. The Balance Between Opportunity and Risk
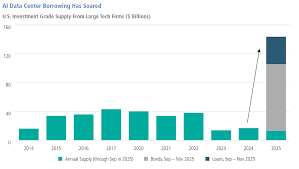
Every individual “The near-record pace of corporate bond issuances is also reflective of both the opportunities and risks that exist at the current time. For example, while access to capital allows corporations to leverage next-generation technologies that have the potential to transform industries and increase productivity,” it also means that corporations have “higher levels of debt that must be managed prudently and realistically.”




